The financial services industry is undergoing a transformative shift fueled by AI-powered data Hospitals like St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, MD Anderson Cancer Center, and Mayo Clinic play a crucial role in advancing medical science through rapid diagnostics, cutting-edge treatment strategies, and drug discovery. Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly becoming an essential tool in these institutions, enhancing diagnostic accuracy, streamlining clinical workflows, and accelerating drug discovery processes.
A research hospital is flooded with data – millions of MRI scans, genomic profiles, and patient records. A clinician is facing a life-or-death case, but even with experience, there’s too much information to analyze manually. What if AI could rapidly sift through it all, identifying patterns that even experts might miss?
That future is no longer hypothetical – it’s happening now. AI can instantly provide genomic insights, treatment outcomes from similar patients, and the latest research on targeted therapies. What once took weeks of manual review can now be accomplished in minutes.
This blog explores how these systems are built, how they interact, and why they are critical to the future of medicine.
The Data Landscape
The scale of data generated in a research hospital is almost unfathomable. Every patient visit, scan, genomic test, and treatment contributes to a constantly growing dataset that fuels medical research, patient care, and AI-driven diagnostics. However, managing this data requires extreme precision – both in terms of fidelity and privacy. A hospital’s AI infrastructure must ensure that patients’ privacy is never compromised while still allowing physicians to leverage massive datasets to identify diagnostic markers, treatment pathways, and optimal care plans.
Before AI, physicians relied on manual comparisons, educated guesses, and limited historical data when treating complex cases. Today, with millions of anonymized patient records, they can analyze trends, correlate genetic mutations with disease progression, and determine the most effective treatments. This shift reduces not only the time required for diagnosis but also the psychological burden on clinicians who previously had to make life-and-death decisions with incomplete information.
The data landscape within research hospitals consists of several key domains:
- Imaging Data: MRI, CT scans, PET scans, and X-rays used in radiology and oncology. AI models analyze these images for disease markers, tumor detection, and treatment response tracking.
- Genomic & Proteomic Data: Whole genome sequencing, RNA sequencing, and proteomic profiling to understand disease mechanisms at the molecular level. This data is crucial for personalized medicine and targeted therapies.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): A structured repository of patient histories, lab reports, clinical notes, prescriptions, and treatment plans. AI can extract insights, predict disease progression, and identify patterns that humans might miss.
- Pathology Data: High-resolution histopathology slides allow AI to detect cancerous cells, autoimmune conditions, and rare disorders through deep learning analysis.
- Wearable & Sensor Data: Continuous patient monitoring generates real-time telemetry on vital signs, glucose levels, ECGs, and other biometric data. AI processes this stream to predict and prevent adverse medical events.
- Clinical Trial Data: AI optimizes patient recruitment, monitors drug responses, and helps researchers analyze efficacy across different demographics and genetic profiles.
- Omics Data Integration: AI-powered multi-modal data fusion—such as combining imaging data with genetic profiles—enables precision medicine, where treatments are tailored to an individual’s biological makeup.
The DDN Infinia Data Lake serves as the backbone of this ecosystem, providing high-speed data persistence and retrieval for these massive, diverse datasets. Unlike siloed traditional database solutions, a unified data lake allows AI models to cross-reference different data types seamlessly, delivering faster query response times, optimized GPU utilization, and enhanced predictive accuracy.
Choosing the Right AI Models &Training in Life Sciences
Selecting the right AI model for a specific challenge—whether it’s drug discovery, MRI analysis, or patient risk prediction—is a critical decision. Life sciences require massive data correlation and multiple iterations of model training to fine-tune accuracy. Using the wrong model could lead to misleading predictions, while choosing the right one can unlock groundbreaking insights. Here’s a breakdown of where different models shine:
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are the gold standard for image analysis. Whether it’s detecting lung cancer in CT scans or identifying abnormalities in pathology slides, CNNs are built to recognize patterns in visual data with high precision.
- Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) excel at modeling relationships between complex entities, such as disease-drug interactions and patient similarity. If the goal is to predict how a drug will interact with a specific genetic mutation, GNNs provide a powerful framework.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) & Transformers handle time-series data exceptionally well. They’re ideal for analyzing patient vitals over time to predict ICU admission risk or tracking how genomic sequences evolve in response to treatment.
- Federated Learning Models enable hospitals to collaborate on AI training while preserving patient privacy. Instead of sharing raw data, hospitals train models locally and exchange insights without exposing sensitive patient records.
Once the right model is selected, researchers follow a structured AI workflow—whether they’re training AI for drug discovery or optimizing MRI diagnostics. The process typically involves:
- Data Collection & Preprocessing: Extracting and cleaning multimodal data, ensuring it’s structured correctly for AI training.
- Model Selection & Training: Iterating through different neural networks, adjusting hyperparameters, and refining predictions.
- Validation & Optimization: Testing models against known cases, fine-tuning parameters to improve accuracy.
- Deployment & Inference: Running AI models in real-world scenarios, integrating them into hospital decision-making pipelines.
- Continuous Learning & Improvement: AI never stops learning—new data refines the model, ensuring it remains cutting-edge.
The following diagram illustrates this high-level AI workflow, highlighting the iterative nature of training and deploying AI in life sciences.

How Data Flows in an AI-Driven Research Hospital
To understand the infrastructure behind an AI-powered hospital, let’s follow the journey of a single clinical query from start to finish.
A doctor logs into the hospital’s AI-powered interface and enters the following request:
“Analyze this patient’s MRI scan and genomic profile. Predict the likelihood of tumor progression and suggest a personalized treatment plan based on similar cases.”
At this point, the system initiates multiple workflows behind the scenes:
- Querying a Graph Database for Patient Similarity
To begin, the AI accesses a graph database, which maps relationships between patients, diseases, genetic markers, and treatment outcomes. By analyzing these connections, the system identifies cases with similar molecular profiles and treatment histories, ensuring a more personalized approach to care. If past patients with the same mutation responded well to a specific immunotherapy, the system flags that as a potential treatment option. - Retrieving Data from Object Storage and Data Lake
Once a similar patient profile is identified, the AI retrieves MRI scans, genomic data, and patient records from a unified data lake. This centralized system eliminates delays, ensuring AI models can instantly cross-reference vast datasets for more accurate and timely predictions. - Enriching the Data with Metadata
As soon as the AI pulls imaging and genomic data from the data lake, metadata is generated, tagging patient IDs, scan types, and AI-driven annotations for instant retrieval. Products like DDN Infinia are critical at this stage to provide metadata indexing which enables rapid retrieval and AI inferencing. - Processing with the ETL Pipeline (DDN Infinia + NVIDIA NeMo)
- Extract: Data is pulled from PACS (imaging), genomic sequencing platforms,and EHRs, leveraging DDN’s parallel processing capabilities to optimize throughput.
- Transform: NLP models powered by NVIDIA NeMo extract insights from clinical notes, while AI-based image segmentation tools detect tumor boundaries.
- Load: Transformed data is efficiently written back into the data lake, ensuring easy reusability for future AI model inference.
- PII/PHI Processing & Security (Zero Trust + Federated Learning)
- De-Identification & Tokenization: Patient data is anonymized before AI models access it.
- Federated Learning: Before any AI training begins, data must remain private. Rather than sharing raw patient records, hospitals use federated learning to train models locally, exchanging only learned insights.
- Homomorphic Encryption: Enables AI models to process encrypted data without decrypting it, preserving patient privacy.
- Choosing the right AI model for the job
As outlined earlier, selecting the right AI model is not just a technical decision—it’s a defining factor in the success of an AI-driven deployment in life sciences. The effectiveness of diagnostics, treatment recommendations, and research outcomes all hinge on this choice, making it one of the most critical steps in building a robust AI-powered healthcare system. - Presenting AI-Generated Insights to the Clinician
The AI assembles findings into a structured report. Because of Infinia’s high-speed metadata indexing, response times are significantly faster than traditional data solutions, ensuring real-time decision-making.
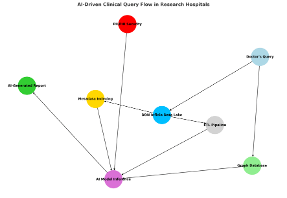
This end-to-end process showcases how AI, when integrated with high-performance data intelligence and intelligent metadata management, can transform research hospitals into fully AI-augmented medical institutions, where precision medicine is faster, more accurate, and more scalable than ever before.
Why a Unified Data Lake is Essential
I’ve seen firsthand what happens when data management goes wrong. When I worked at one of the largest custodian banks in the U.S. data sprawl was a constant nightmare. Every time a developer needed data, they would just copy an entire database rather than accessing a shared source. Over time, this led to hundreds of redundant copies of the same data scattered across the organization.
The problem? Besides being a massive waste of resources, these copies quickly became stale. If data was updated in one place, every other copy became outdated, leading to inconsistencies across systems. Reconciling all these versions was nearly impossible – without a central architecture, it was like trying to piece together a puzzle where half the pieces were missing.
Just like in banking, hospitals and research institutions struggle with fragmented data—imaging files, genomic records, and patient histories scattered across multiple systems. Without a unified approach, inconsistencies arise, slowing research and compromising patient care.
- Eliminating Redundant Data Copies
Instead of duplicating databases across silos, a unified data lake centralizes everything in one high-performance, scalable system. This eliminates inefficiencies and ensures that all AI models, researchers, and clinicians are always working with the same, most up-to-date version of the data. - Optimizing AI Compute Utilization
In traditional setups, AI models can spend 40% or more of their processing time just waiting on slow data feeds. When data is fragmented across multiple systems, it forces constant lookups, slowing down retrieval speeds and delaying real-time analysis. DDN Infinia streamlines this by ensuring that AI has instant access to data, allowing for real-time execution without bottlenecks. - Enabling Long-Term AI Evolution
AI isn’t a “train once and forget it” system – it needs to be continuously retrained on the latest data. A unified data lake supports incremental learning, allowing models to evolve without needing to restart from scratch every time. This keeps AI predictions sharp and aligned with the most current patient data, research findings, and treatment trends.
All Data Lakes are not Created Equal:
At the end of the day, data silos and redundant copies are a legacy burden that research hospitals can no longer afford. DDN Infinia provides a scalable, high-performance solution that ensures accuracy, efficiency, and real-time AI-driven decision-making – without the chaos of fragmented data.
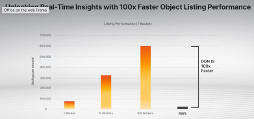
AI models process billions of objects daily, but in traditional cloud environments (like AWS S3, GCS or Azure Blob) just listing these objects creates a major bottleneck. This isn’t just a data access problem – it’s an AI performance bottleneck. A slow data pipeline means missed diagnoses, delayed treatments, and wasted GPU cycles. DDN Infinia eliminates these inefficiencies, allowing hospitals to focus on delivering better patient outcomes instead of waiting on infrastructure limitations.
DDN Infinia delivers up to 100x faster performance than AWS S3 by optimizing metadata handling and parallel processing. This means AI models can access data instantly, accelerating real-time decision-making.
The graph below shows exactly why DDN is built for AI at scale.
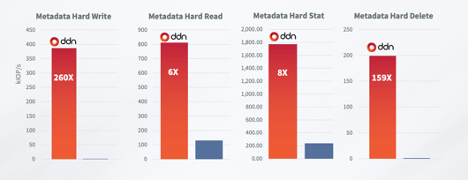
Similarly, DDN’s ability to accelerate a variety of data processing tasks – typical of data pre-processing; creating, manipulating and removing data objects rapidly is proven to be much faster than competing systems:
Conclusion
AI-driven research hospitals handle an unprecedented volume of data across imaging, genomics, clinical notes, and real-time biometrics. The ability to extract insights from this data at scale transforms disease diagnosis, treatment personalization, and drug discovery.
With DDN Infinia’s AI-optimized data lake, hospitals can consolidate and analyze petabyte-scale workloads in real-time, enhancing precision medicine while maintaining stringent security, privacy, and efficiency.
The future of AI in research hospitals is about scalability, security, and trust—and with DDN Infinia, that future is already here.



